LeetCode in Net
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Hard
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
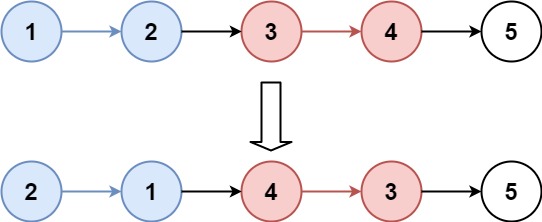
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:
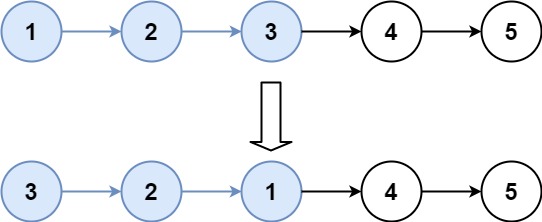
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1], k = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
sz. 1 <= sz <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 10001 <= k <= sz
Follow-up: Can you solve the problem in O(1) extra memory space?
Solution
using LeetCodeNet.Com_github_leetcode;
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null || k == 1) {
return head;
}
int j = 0;
ListNode len = head;
// loop for checking the length of the linked list, if the linked list is less than k, then return
// as it is.
while (j < k) {
if (len == null) {
return head;
}
len = len.next;
j++;
}
// Reverse linked list logic applied here.
ListNode c = head;
ListNode n = null;
ListNode prev = null;
int i = 0;
// Traverse the while loop for K times to reverse the nodes in K groups.
while (i != k) {
n = c.next;
c.next = prev;
prev = c;
c = n;
i++;
}
// `head` is pointing to the 1st node of the K group, which is now going to point to the next K group
// linked list.
// Recursion for further remaining linked list.
head.next = ReverseKGroup(n, k);
return prev;
}
}

